When it comes to building or upgrading a PC, understanding the harmony between a CPU (Central Processing Unit) and a GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) is crucial. The question “Is my CPU bottlenecking my GPU?” resonates with many PC enthusiasts and gamers.
Today, I will explore this question in-depth, providing insights into how processors and graphics cards work together, how to identify a bottleneck, and steps to achieve a balanced system.
CPU-GPU Bottlenecks Explained
- Concept of Bottlenecking: In computing, a bottleneck occurs when the performance of an entire system is limited by a single component. In the context of CPUs and GPUs, a bottleneck happens when one of these components is not fast enough to keep up with the other, leading to underutilization and inefficiency.
- CPU vs. GPU Roles: The CPU, often termed the brain of the computer, handles general-purpose tasks and feeds data to the GPU. The graphics card, specialized in parallel processing, excels in rendering graphics. A mismatch in their performance can lead to bottlenecks.
- Impact on Performance: A bottleneck can significantly impact system performance, especially in graphics-intensive tasks like gaming or 3D rendering. It’s essential to understand how these components interact to maximize their potential.
Identifying a Bottleneck
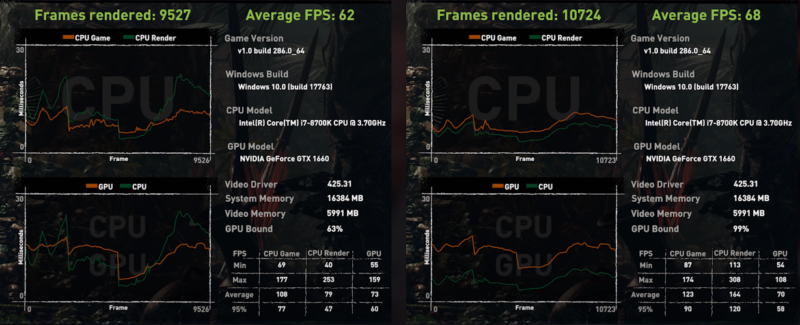
- Monitoring Tools: Use software tools to monitor CPU and GPU usage while running various applications. If one component is consistently at high usage while the other is underutilized, it’s a sign of a bottleneck.
- Performance Metrics: Pay attention to frame rates in games and rendering times in applications. If these metrics are lower than expected based on the specifications of the graphics card, the processor might be the bottleneck.
- System Behavior Analysis: Notice if there are inconsistencies in performance, such as stuttering in games or slow application response during high-demand tasks. These can indicate a CPU struggling to keep up with the GPU.
Factors Contributing to Bottlenecks
- CPU-GPU Balance: The key to avoiding bottlenecks is balance. A high-end GPU paired with an older, less powerful CPU is a common mismatch.
- Task Nature: Different tasks stress the processor and graphics card differently. Games with complex physics and AI are processor-intensive, while graphically rich games put more load on the GPU.
- Background Processes: Running multiple applications or having numerous background processes can strain the CPU, impacting its ability to feed the GPU efficiently.
Enhancing Your System’s Performance
Upgrading Components
- When to Upgrade: Consider upgrading the CPU if it’s significantly older or less powerful than the GPU. Similarly, upgrade the GPU if it’s the weaker link in the system.
- Compatibility Checks: Ensure that the new component is compatible with your existing system, particularly the motherboard and power supply.
- Balancing Budget and Performance: Aim for a balance between performance and cost. Sometimes, a modest upgrade can significantly reduce bottlenecks.
Optimizing Software and Settings
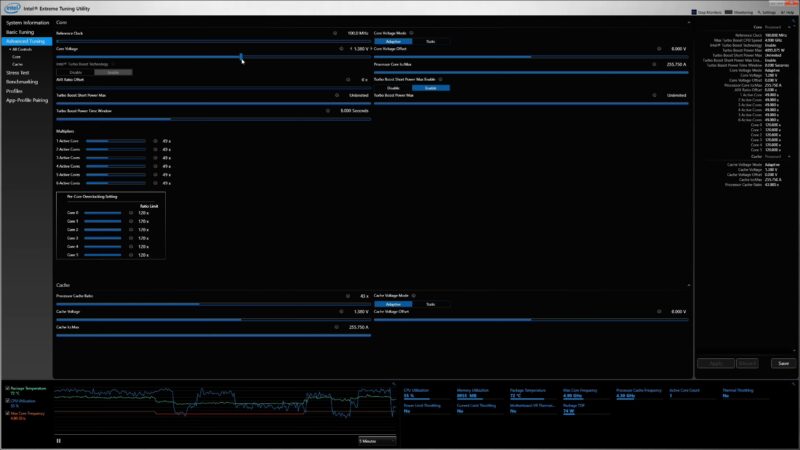
- Operating System Optimization: Keep the operating system and drivers updated. Close unnecessary background applications to free up CPU resources.
- Game and Application Settings: Adjust graphics settings in games and applications to better match your system’s capabilities. Lowering resolution or detail can reduce GPU load, while decreasing draw distance or AI complexity can ease CPU strain.
- Overclocking: Overclocking the CPU or GPU can squeeze out extra performance, but it requires careful consideration of cooling and power requirements.
Future-Proofing Your System
- Investing in High-Quality Components: Choose components that offer a good balance of current performance and future scalability.
- Staying Informed: Keep up with technological advances to understand when upgrades might be necessary.
- Regular Benchmarking: Regular benchmarking your system can help identify performance trends and potential bottlenecks over time.
Balancing CPU and GPU for Different Use Cases
Gaming Performance
- Gaming Demands: Modern games demand a lot from both processors and graphics cards. High-resolution textures and complex environments push GPUs, while AI, physics, and multiple characters challenge CPUs.
- Choosing the Right Pair: For a gaming rig, balance is key. A powerful GPU for PC paired with a mid-range CPU can handle most games well. However, for CPU-intensive games or high frame rate targets, a stronger CPU becomes essential.
- Adjusting for Optimal Performance: Gamers should adjust in-game settings to find a balance that maximizes frame rates without overloading the CPU or GPU.
Professional Workloads
- Workstation Requirements: Professional applications like video editing, 3D rendering, and data analysis have diverse requirements. Some are GPU-heavy, like 3D rendering, while others, like data analysis, rely more on the CPU.
- Workstation Component Selection: For workstations, the choice depends on specific application needs. A high-end CPU is crucial for software that relies on fast processing, while a robust GPU is needed for tasks like video rendering.
- Balancing for Efficiency: In professional settings, efficiency and time are critical. Balancing CPU and GPU ensures that tasks are completed quickly without unnecessary delays or crashes.
General Computing
- Everyday Computing Needs: For general use, such as web browsing, office applications, and media playback, the demands on both processor and graphics card are relatively low.
- Cost-Effective Choices: In these cases, a balanced, cost-effective approach is suitable. A mid-range CPU paired with an integrated or low-end GPU is often more than enough.
- Optimization for Smooth Operation: Regular maintenance, like updating software and cleaning up background processes, can keep a general-use PC running smoothly without needing high-end components.
Advanced Techniques to Address Bottlenecks
Hardware Overclocking
- Know the Overclocking Process: Overclocking means pushing your CPU or GPU beyond its standard operating frequency, providing a temporary solution to bottlenecks.
- Risks and Rewards: While overclocking can improve performance, it also increases heat and power consumption and may reduce the lifespan of components.
- Doing It Right: If you decide to overclock, use reliable tools and proceed cautiously, monitoring temperatures and system stability.
Software Optimization
- Customizing Settings: In many applications, especially games, adjusting settings can significantly impact performance. Lowering resolution, texture details, or shadow quality can alleviate GPU bottlenecks while reducing view distance or physics details can help a struggling CPU.
- Updating Drivers: Keeping GPU and CPU drivers up-to-date can improve performance and compatibility, potentially easing bottlenecks.
System Maintenance
- Keeping the System Clean: Physical maintenance, like cleaning dust from vents and fans, helps maintain optimal cooling, which is crucial for performance.
- Operating System Health: Regularly cleaning up the hard drive, defragmenting (for HDDs), and scanning for malware can keep the operating system running efficiently, reducing unnecessary CPU and GPU stress.
FAQs
Can a powerful GPU compensate for a weaker CPU in gaming?
No, a powerful graphics card cannot fully compensate for a weaker CPU in gaming. While the GPU handles graphics, the CPU is responsible for overall game logic, physics, and AI, which are crucial for a smooth gaming experience.
Does increasing game resolution put more load on the CPU?
No, increasing game resolution primarily increases the load on the GPU, not the CPU. The CPU load is more affected by game mechanics and the number of objects or characters in the game.
Can upgrading RAM alleviate a CPU bottleneck?
Upgrading RAM can help only if the bottleneck is due to insufficient memory. If the CPU itself is underpowered for the tasks, more RAM will not resolve the bottleneck.
Is it possible for a CPU to bottleneck a GPU in simple tasks like web browsing?
It’s unlikely for a CPU to bottleneck a GPU in simple tasks like web browsing, as these tasks are generally not demanding enough to cause such an imbalance.
Do I need to replace both my CPU and GPU to fix a bottleneck?
Not necessarily. You may only need to upgrade the component causing the bottleneck. Identifying which component (processor or graphics card) is underperforming is key.
Can bottlenecking cause damage to my CPU or GPU?
Bottlenecking itself doesn’t cause physical damage to your CPU or GPU. However, it can lead to inefficient system performance and potentially cause overheating if one component is consistently overworked.
Final Words
Identifying and addressing CPU-GPU bottlenecks is a dynamic process that requires a balance of hardware and software optimization.
Knowing how these components interact, monitoring performance, and making informed upgrades will allow you to ensure that your system operates at its full potential.
Remember, the goal is to achieve a harmonious relationship between your CPU and GPU, maximizing the performance and enjoyment of your computing experience.

